Dear Editor,
IgA vasculitis (IgAV) refers to IgA1 immune complex-mediated inflammation of cutaneous, renal, and gastrointestinal (GIT) microvasculature. Recognised primarily in children as Henoch Schonlein Purpura/ anaphylactoid purpura; it presents with a tetrad of palpable purpura, arthritis, haematuria, and abdominal pain. The adult counterpart is less well characterised with an incidence of 1.3-1.4/1,00,000/year.1 It can be triggered by upper respiratory infections, vaccinations, and drugs like ampicillin, quinine, and infliximab.2
It is imperative for dermatologists to acknowledge this condition, as they have a heightened risk of developing end-stage kidney disease (ESKD) compared to children who experience self-limiting trajectory..2,3 A one-year retrospective record review was conducted on patients over 18-years of age diagnosed with IgAV based on European league against rheumatism (EULAR) criteria [Table 1].4
Table 1: European league against rheumatism (EULAR) criteria* for diagnosis of IgA vasculitis
Criteria Definition 1. Purpura Palpable purpura, often in crops over-dependent areas, non-thrombocytopenic 2. Gastrointestinal (GIT)# Abdominal pain (acute onset, colicky), other features include GIT bleeding and intussusception 3. Biopsy (Either Skin or renal) Leukocytoclastic vasculitis/ proliferative glomerulonephritis AND predominant mesangial IgA deposition 4. Joint Acute onset arthritis (swelling, pain, restriction of motion) or arthralgia (pain) 5. RenalProteinuria >0.3gm/day
Hematuria (>5 red blood cells/high power field or red cell casts)
A total of six cases were reviewed for clinical and investigation details [Table 2]. Their mean age was 28 years with a male-to-female ratio of 5:1. All patients had cutaneous onset with joint involvement in 4 patients; GIT and renal involvement were present in 3 patients.
Table 2: A summary of the IgA vasculitis cases in the present study.
Case Age/Sex Organ involvement Skin lesions Biopsy and investigations Treatment* Outcome# Recurrence 1 33/M Skin-Joints-Renal Palpable purpura, targetoid lesions over elbows and lower limbs LCV in dermal capillaries along with granular IgA deposits on DIF Prednisolone* and DapsoneSkin lesions and joint complaints resolved in 3 weeks
Renal parameters normalised by 1 month
No 2 35/F Skin-Joints-GITPurpuric lesions, hemorrhagic necrotic and pustular lesions over both upper and lower extremities and trunk
Erosions over tongue
LCV in dermal capillaries, IgA, IgM, C3 deposition on DIFPrednisolone and cyclosporine
Initially managed with Dapsone, which was stopped due to development of DRESS
Lesions healed in 2 months
GIT symptoms and joint complaints resolved in 2 weeks
No, maintained on treatment 3 22/M Skin-GITPalpable purpura over upper and lower limbs, urticated papules over the trunk.
Gingival hypertrophy with sterile pustules over dental apices
LCV in dermal blood vessels, DIF-granular IgA and IgM deposition
CT abdomen revealed circumferential thickening of jejunum and ileum, colonoscopy revealed ileal erosions and nodularity with dense infiltrate without any granulomas.
Prednisolone and Dapsone Skin lesions and GIT complaints initially resolved in 3 weeksYes (cutaneous relapse) at 3 months, managed with prednisolone and dapsone.
Treatment stopped after one year after a symptom-free period of 6 months.
4 25/M Skin-Joints-GIT Palpable purpura, urticated papules over lower and upper limbs LCV in upper dermal capillaries, IgA granular deposits on DIF Prednisolone and DapsoneLesions cleared by one month
Joint and GIT complaints resolved by 1 month
No 5 25/M Skin-Joints-Renal Purpuric, hemorrhagic, and necrotic lesions over both upper and lower extremities Lymphocytic infiltrate with LCV, IgA 3+ positivity in dermal capillaries on DIFPrednisolone, telmisartan,
furosemide
Skin lesions resolved without treatment, Improvement in frothuria and proteinuria No 6 29/M Skin-Renal Purpuric lesions over legs LCV with IgA 2+ positivity in dermal capillariesPrednisolone, telmisartan,
furosemide
Skin lesions resolved within 14 days of therapy. Improvement in frothuria noticed over 2 months No, maintained on treatmentAdult-onset IgAV has cutaneous manifestations in 75% cases, mainly asymmetrical palpable purpura involving gravity-dependent areas, sometimes extending to the upper limbs and trunk. It presents with diverse morphologies, including bullous, ulcerative, pustular, hemorrhagic purpura, and urticated papules.5 All our cases had cutaneous onset with extensive purpuric lesions on extremities with targetoid lesions [Figure 1a–1c]. Mucosal involvement was observed in two patients (oral erosions, sterile gingival pustules).
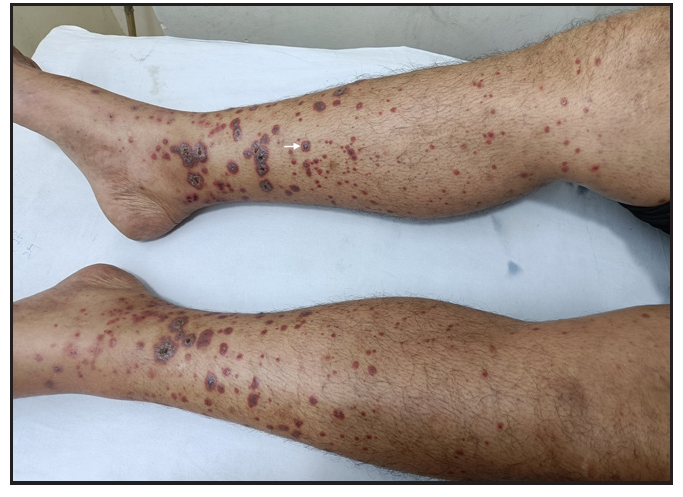
Export to PPT
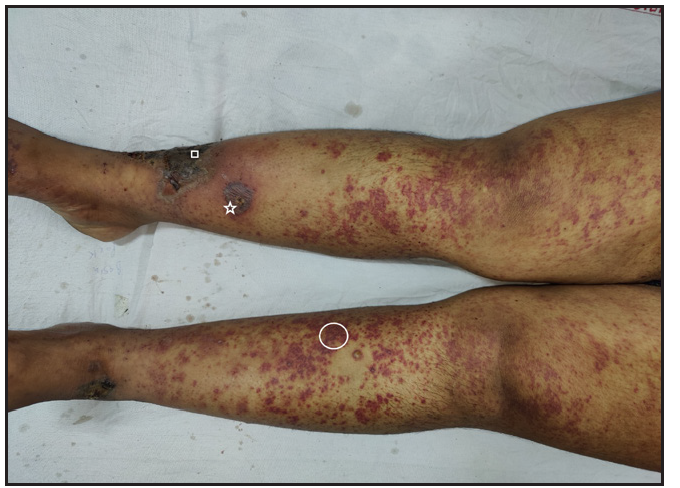
Export to PPT
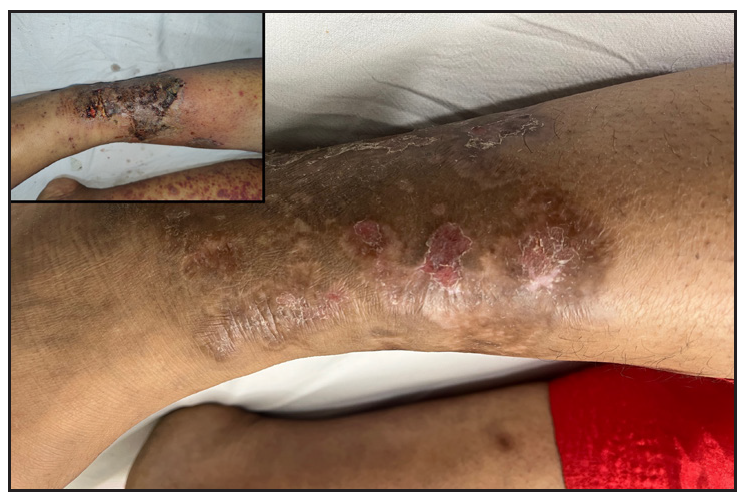
Export to PPT
The diagnosis of IgAV requires either skin or renal biopsy for evidence of LCV (leukocytoclastic vasculitis).4 Skin biopsy shows LCV in postcapillary venules along with IgA and C3 deposition with a sensitivity of 81%, specificity of 83-85%, and positive and negative predictive values of 81% and 84%, respectively [Figure 2a–2b].5 In a study, IgAV was the commonest diagnosis (31%) among 198 analysed cases of cutaneous small-vessel-vasculitis; clinical diagnosis of IgAV could be confirmed in 61.5% cases by direct immunofluorescence (DIF), and in remaining unsuspected cases, diagnosis of IgAV was based solely on DIF findings.6
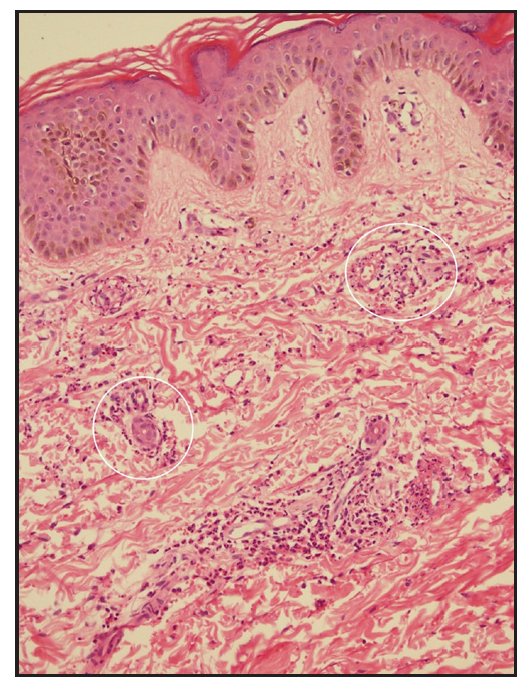
Export to PPT
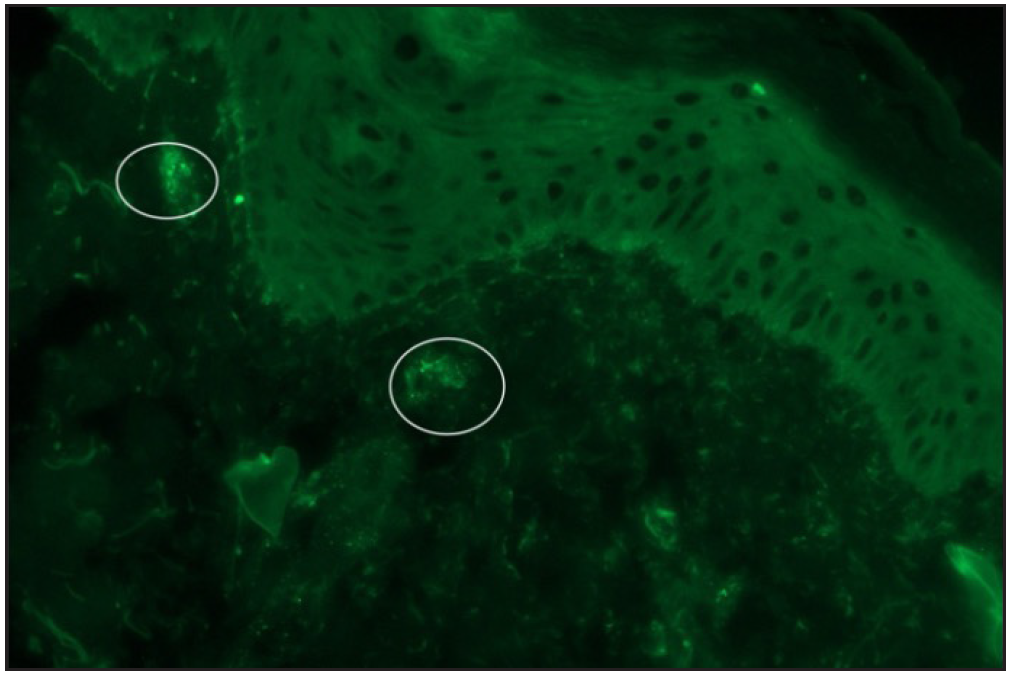
Export to PPT
Regarding extracutaneous manifestations, an Asian cohort demonstrated renal involvement in 56%, joint and GIT involvement in 31% each.7 Joint involvement is transient, oligoarticular, and non-deforming, affecting large joints of lower limbs. GIT involvement includes abdominal pain, intestinal bleeding, diarrhoea, and acute abdomen. Rarely associated with Crohn’s disease, IgAV usually presents with mucosal erythema or ulcerations in the duodenum/ileum, sometimes manifesting as isolated terminal ileitis (patient 3). Crohn’s disease, on the other hand, presents with fissures, small bowel strictures, transmural inflammation, and non-caseating granulomas.
Renal involvement in IgAV presents with severe proteinuria, haematuria, or renal failure.3,5 Risk factors include female gender, older age of onset, haemorrhagic lesions above the waistline, GIT symptoms, relapses, leukocytosis, and low C3 levels.2,3,5 Non-invasive biomarkers like neutrophil-lymphocyte ratio, urinary IgA, and interleukins-6, 8 can predict renal involvement.8 The presence of additional IgM and C3 deposits in the skin may predict renal and joint involvement, respectively.8
Renal biopsy is reserved for persistent proteinuria, nephrotic or nephritic syndrome, and renal failure. It helps to differentiate from other pathologies and is not meant for initial diagnosis. Skin biopsy and DIF are recommended by EULAR for use in initial diagnosis.4,8
IgAV should be differentiated from IgA nephropathy (IgAN), a renal-limited form, mandating renal biopsy, presenting with macroscopic hematuria and often being diagnosed at ESKD. Skin biopsy in IgAV may rarely show IgA deposits, which are considered non-diagnostic and lack sensitivity as a diagnostic tool.
Treatment is recommended for all adults due to a higher risk of severe renal disease (35-69%) compared to children (5-20%). Non-steroidal-anti-inflammatory drugs should be avoided due to the risk of renal disease and GIT bleeding.5 Management of skin-limited IgAV involves rest, leg elevation, low-dose prednisolone, and colchicine in patients without GIT symptoms.5 In non-responsive cases, dapsone or azathioprine can be added. For joint involvement, oral acetaminophen is advocated along with steroids in severe disease.
For renal disease, angiotensin-receptor blockers targeting 24-hr urine protein <1 gm, and blood pressure <130/80 mm Hg are recommended with limited use of immunosuppressants for persistent proteinuria. Elderly adults have unfavourable prognosis, with 7-fold mortality, often due to associated solid organ or hematological malignancy.3 Relapse (in 15%) is associated with early onset, joint involvement, and lack of immunomodulatory treatment; it is most often a cutaneous relapse, as observed in patient 3 in our series. Long-term follow-up with symptom screening, urine analysis, and serum creatinine fortnightly for 1 month followed by 2 monthly for 1 year is prudent.
To conclude, adult IgAV needs extensive literature contributions from diverse medical specialties and geographical regions for more information to optimise management strategies. Adults can present with diverse and extensive cutaneous lesions above the waistline. Additionally, patients have an increased propensity for renal and GIT involvement.
Comments (0)